94% of organizations say customers won’t buy from them if they don’t protect user data suitably. This stat from the Cisco “2024 Data Privacy Benchmark Study” perfectly captures the current state of affairs in the business world: Privacy is where our focus must be.
42DM has worked with global customers in diverse niches, designing and putting into practice customized lead-generation strategies that both convert leads and safeguard their privacy. In our experience, this process is challenging but highly rewarding for businesses. Here, we’ll gladly share what we’ve learned so far, hoping that it helps you achieve your marketing goals while building an even more privacy-conscious tomorrow.
This article discusses the data privacy challenges in inbound lead generation, the cornerstone of today’s marketing and business strategies. You’ll learn:
- Why businesses have adopted a data-driven approach in inbound lead generation
- The challenges they face in implementing it
- The central role of data privacy regulations in the contemporary marketing climate
- Tips on choosing privacy-compliant marketing solutions and building privacy-first inbound marketing
The role of data in inbound lead generation
Data has become the pillar of inbound lead generation, and rightly so. Basing your marketing strategies on hard data rather than assumptions and guesses puts you in an almost perfect position to:
- Understand customers and their pain points.
- Identify behavioral patterns and emerging trends.
- Create targeted content and personalize outreach.
- Refine messaging and optimize marketing campaigns.
Whether through SEO optimization, email segmentation, or predictive analytics, businesses using data effectively can make informed decisions that attract, nurture, and convert high-quality prospects. Simultaneously, they can minimize the risk of wasting resources on unqualified prospects.
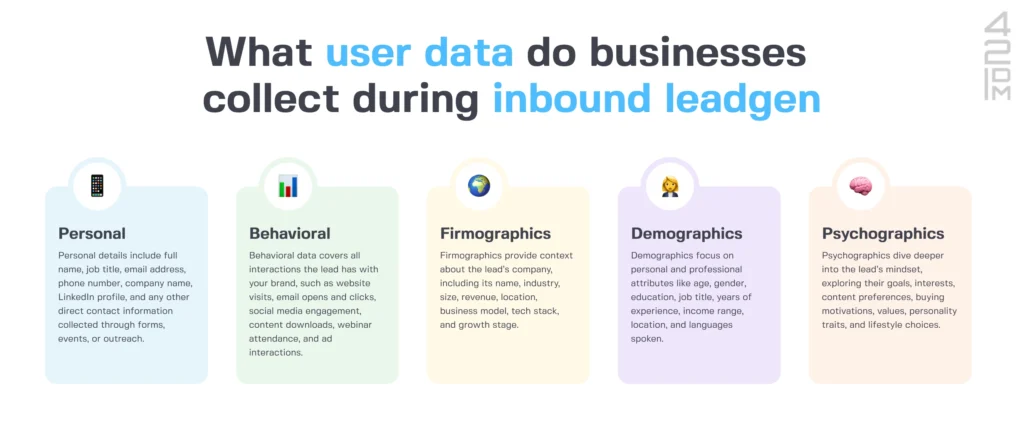
The data that businesses collect falls within several categories:
- Personal details, including names, email addresses, and phone numbers
- Behavioral data, like page views, click-through rates, and social media shares
- Firmographics, such as the lead’s company size, niche, and location
- Demographics, that is, details like the lead’s age, gender, and occupation
- Psychographics, meaning information about users’ interests, preferences, and values
However, as businesses seek to make their inbound lead generation strategies data-driven, they must strike the right balance between this marketing approach and data security. Indeed, consumers today expect relevant and customized experiences, but they also require an assurance that organizations collect and use their data ethically—without jeopardizing privacy.
For this reason, businesses must endorse transparency, ensure that data collection complies with regulations, and communicate clearly how the gathered information improves user experience. They can deliver meaningful marketing that builds lasting relationships with customers only by adopting ethical data handling practices and maintaining a healthy balance between personalization and privacy.
Top data privacy challenges in lead generation
Data-driven inbound lead generation has gained so much traction for a simple reason: It works. However, marketing relying on data has raised serious privacy concerns. And it’s not just breaches that make people’s hair stand on end. It’s also the way businesses collect and handle user data.
These concerns gave rise to a new legislature that strives to protect people’s data rights. The way we see it, these regulations are the foundation on which rest, more or less, all the new marketing practices and approaches. Or better, these laws embody and verbalize the general principles that we all—as users, not just marketers—feel must apply to how we do marketing today.
So, what are the data privacy challenges in today’s lead generation?
Compliance with global privacy regulations
Data privacy compliance is one of those challenges, and the requirements most relevant for inbound lead generation are:
- GDPR (EU)
- The opt-in forms must have straightforward consent checkboxes.
- Businesses must have a legal basis to collect and process data.
- Retargeting and email marketing require explicit user consent.
- CCPA (California, USA)
- Businesses must include a “Do not sell my personal information” link.
- The collected data must be clearly disclosed and deletable upon request.
- Lead data from third-party sources must be properly documented.
- CPRA, aka CCPA 2.0 (California, USA)
- This regulation builds upon CCPA to define stricter rules for storing and using data and improve user control over personal information
- CAN-SPAM Act (USA)
- Emails must provide an explicit opt-out.
- Cold outreach must follow honest marketing practices.
- CASL (Canada)
- Businesses cannot send marketing emails without previous user consent.
- The proof of consent must be documented.
- PECR (UK)
- Lead capture forms and cookies must have explicit consent options.
- Businesses cannot do cold outreach without previous lead consent (except in B2B cases).
- LGPD (Brazil)
- Businesses must get consent before collecting lead data.
Non-compliance with these privacy regulations leads to:
- Fines, such as €20M or 4% of revenue (GDPR), $10M (CASL), $50,120 per email (CAN-SPAM), or $7,500 per violation (CCPA)
- Business restrictions, that is, regulatory bodies banning you from collecting or processing personal data
- Reputation damage, resulting in the loss of customer trust, negative press, and eventually customer loss
- Data breaches because of poorly protected data leading to hacks, fraud, and identity theft
- Legal actions and lawsuits, especially in cases of flagrant violations of compliance requirements leading to data theft
- Loss of partnerships primarily due to the ethical connotation of disregarding the sanctity of people’s privacy

Collecting and storing data securely
Unsecured data is a risky affair, even without the threat of fines for non-compliance.
Breaches, data theft, leaked information, intercepted communication, phishing campaigns, and ransomware all pose a direct threat to your leads’ data. For this reason, you must make sure that the information you collect and store is suitably secured both in transition and at rest through robust security measures, such as:
- Strong encryption algorithms/technologies like AES-256 and TLS
- MFA (multifactor authentication)
- RBAC (role-based access control)
- Log audits and real-time monitoring
- Automatic logouts for inactive sessions
- Data classification
- Data masking or tokenization
- Safe and properly inventoried APIs
Speaking of APIs, keep in mind that third-party tools, apps, CRM platforms, and, generally, integrations can be a liability as well as an asset. Hence, one of the first pieces of advice we give our customers is to ensure their third-party marketing tools and CRMs:
- Rely upon secure APIs for data exchange
- Are compliant with global standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and the Privacy Shield Framework
- Allow data access, deletion, and rectification
- Apply end-to-end encryption
- Have a breach response plan in place
- Have limited access to your information environment
Gaining explicit consent without hurting conversion rates
Opt-ins and cookie policies are essential for compliance and user trust. They allow businesses to boost conversion rates without causing ethical issues in data collection.
However, poorly implemented marketing consent mechanisms—such as intrusive pop-ups and confusing language—create disharmony in the user journey and can negatively affect conversion. The solution for our customers was to present clear, nonintrusive, and easily understandable opt-in choices that explain how data will be used without overwhelming the user.
To optimize both compliance and conversions, businesses should use layered consent banners that briefly explain data collection upfront, with an option to view more details. Pre-ticked checkboxes are a no-go under GDPR, so instead, forms should feature concise, user-friendly checkboxes that clarify benefits (say, “Stay updated with expert insights—opt in for our newsletter”).
Also, some of our clients have shared that progressive marketing consent models, where users grant permissions gradually rather than all at once, have helped a lot with reducing drop-offs.
HubSpot and Slack are good examples of user-friendly forms. HubSpot’s lead capture forms include a simple, optional checkbox for marketing emails. That keeps things clear while ensuring a good user experience. Slack’s sign-up process offers an easy opt-in that assures users their data will be safe.
By embodying compliance into a conversion-friendly design, businesses can build trust and maximize engagement.
Third-party data risks in B2B marketing
Using third-party lead databases can be a risky choice. In our experience, many bought contact lists have outdated, incorrect, or non-compliant data. That means wasted outreach efforts and possibly legal problems.
Also, third-party lists often lack verifiable consent records. Besides, email providers and CRM platforms may flag cold outreach campaigns as spam, which damages your domain reputation and deliverability.
Data brokers and enrichment tools introduce additional compliance risks if they collect or aggregate personal data and sensitive data without clear user consent. Some enrichment platforms scrape public profiles or purchase data from unverified sources, which violates privacy laws.
To minimize risk, B2B marketers should:
- Vet third-party vendors carefully and ensure they provide Data Processing Agreements (DPA).
- Use compliant enrichment tools that only process publicly available opt-in data.
- Rely on first-party intent data, such as website interaction, webinar participation, or CRM insights.
- Adopt a zero-party data approach, where leads willingly share their preferences in exchange for concrete value.
Instead of relying on bulk databases, you should prioritize first-party data collection through gated content, event sign-ups, and personalized lead-generation strategies. We’ve had many projects where focus on first-party and ethical data collection helped businesses build trust, improve targeting, stay compliant, and drive noticeable marketing success.
Data ownership and user rights
Data ownership and user rights are at the heart of contemporary privacy laws. Regulations strive to put control back in the hands of users by mandating businesses to offer simple mechanisms to access, change, and delete data effortlessly and at any time.
Automated data request portals, simple workflows for changing or deleting data, and clear communication response times can help you avoid legal issues and operational delays. In addition, offering straightforward ways for leads to opt in and adopting privacy-first inbound strategies like minimal data retention help build stronger, more loyal customer relationships.
Sometimes, data privacy regulations seem like obstacles to getting new leads. But, in practice, they help your marketing efforts. Adhering to rules allowed our clients to focus on quality over quantity, that is, connect only with leads who are genuinely interested in their businesses.
How to build a privacy-first inbound lead generation strategy
To overcome data privacy challenges in lead generation, we need a privacy-first approach. That entails carrying out open data collection and policies, using first-party and zero-party data, practicing secure lead nurturing and retargeting, and opting for privacy-compliant marketing platforms and tools.

Implementing transparent data collection and policies
Concise privacy policies that explain how you collect, store, and use data go a long way toward building trust and meeting compliance requirements. And language that avoids vague phrases and confusing legal terms is the way to go.
Beyond the policy itself, you must proactively inform users about data use through visible consent banners, short disclaimers on lead forms, and preference centers that allow users to customize their data-sharing options.
Risking to be repetitive, here are the best practices for transparent data collection that work for our clients:
- Use plain language: Avoid highly technical legal jargon and provide clear explanations.
- Summarize key points: Offer a short version of privacy policies with an option to read the full details.
- Make consent explicit: Use unchecked opt-in boxes and explain the purpose of data collection.
- Provide easy access: Link privacy policies on every form, email footer, and website page.
- Offer control options: Allow users to update preferences, opt out, or request data deletion at any time.
By following these best practices, you can turn privacy compliance into a competitive advantage and prove your commitment to ethical data handling practices.
Leveraging first-party data and zero-party data
First-party data—gathered from user interaction, such as website visits and form submissions—offers high accuracy and personalization possibilities. Zero-party data, where leads willingly share their preferences and interests, provides deep marketing insights into users’ needs and wants without invasive tracking.
Examples of good first- and zero-party lead-generation tactics are the following:
- Gated content: Offer valuable resources like e-books and whitepapers in exchange for user opt-in.
- Interactive quizzes and surveys: Let users share preferences in a fun, engaging way.
- Newsletter sign-ups: Provide industry insights or exclusive offers to drive organic subscriptions.
- Loyalty and referral programs: Encourage users to share information willingly in exchange for perks.
- First-party analytics: Use privacy-compliant tracking for insights.
- Webinars and live events: Collect attendee information through registration.
- Conversational marketing through chatbots and AI assistants: Engage leads in real time to receive valuable information without intrusive tracking.
Secure lead nurturing and retargeting
By now, it’s clear that to nurture leads without violating GDPR, CCPA, or other laws, you should prioritize consent-based engagement, leveraging first-party data collected through opt-ins, email subscriptions, and gated content.
It’s worth noting that AI and automation can help this process and take personalization to the next level, but only when using anonymized or aggregated data.
To retarget leads safely, without regulatory violations, you should:
- Use first-party data from CRM and marketing automation tools.
- Implement consent-based email nurturing.
- Leverage contextual advertising rather than cookies for ad targeting.
- Deploy server-side tracking with explicit user consent.
- Create custom audience segments from opted-in users for remarketing.
- Offer a clear opt-out option for all retargeting campaigns.
Choosing privacy-compliant tools & platforms
Selecting the right marketing tool requires effort on your side.
Before choosing a platform, you need to evaluate its personal information protection measures, compliance certifications, and user control features. You should also audit vendors by reviewing DPAs, encryption standards, and data retention policies. Our clients typically look for solutions that offer explicit consent mechanisms, secure data transfers, and transparent data-handling practices.
Examples of great privacy-friendly marketing technology solutions are the following:
- CRM:
- HubSpot (GDPR-compliant)
- Zoho CRM (CCPA-friendly)
- Pipedrive (ISO 27001-certified)
- Marketing automation:
- ActiveCampaign (privacy-first)
- Mailchimp (SOC 2 compliant)
- Brevo (formerly Sendinblue, GDPR-certified)
- Analytics:
- Matomo (self-hosted alternative to Google Analytics)
- Fathom Analytics (privacy-focused)
- Consent management:
- OneTrust (enterprise-grade)
- Cookiebot (GDPR-compliant)
- Termly (small business-friendly)
Future trends: How data privacy will shape inbound marketing
With cookies declining and a cookieless future coming, businesses must rely on direct user interaction to gather actionable data. From that perspective, cookieless tracking methods, like contextual advertising and server-side tagging, will become the new norm, allowing marketers to deliver personalized experiences in a new way.
AI-driven privacy-compliant personalization is also emerging as a powerful method of balancing user rights with marketing effectiveness. Machine learning models can analyze aggregated, anonymized data to detect behavioral patterns without storing personal identifiers.
Techniques like differential privacy and federated learning enable brands to offer personalized content and recommendations. In that spirit, AI will be the key to automating marketing consent management and optimizing messaging, along with ensuring ethical data usage in marketing campaigns.
Future policies may introduce shorter data retention periods, stricter consent mechanisms, and broader global enforcement, making it even more challenging to capture and nurture leads.
Nonetheless, businesses that proactively implement privacy-first inbound marketing will stay relevant and be able to gain a competitive edge. Instead of relying on volume-driven outreach, they will prioritize quality engagement, verified intent signals, and secure data infrastructure to stay ahead in the privacy-conscious era.
Conclusion
Contemporary inbound lead generation faces challenges such as stricter data regulations (e.g., CCPA and GDPR compliance laws), reduced tracking capabilities due to cookie deprecation, and declining consumer trust in data collection.
Businesses must prioritize ethical, secure, and compliant marketing and:
- Use direct data from customers and website visitors.
- Provide straightforward ways for people to give their consent.
- Focus on methods and content that naturally draw in potential customers.
- Use server-side tracking, contextual targeting, and AI-driven analytics to maintain personalization without compromising privacy.
Ultimately, a trust-based, compliance-first approach ensures sustainable, high-quality lead generation while guaranteeing customer data protection.
Download inbound marketing guide